THC and HHC work with our body’s natural endocannabinoid system, but how does it work?
The Cannabis plant has been used for thousands of years, but it is only in recent years that we have discovered how THC, HHC, and other cannabinoids interact with our bodies.
How does it work?
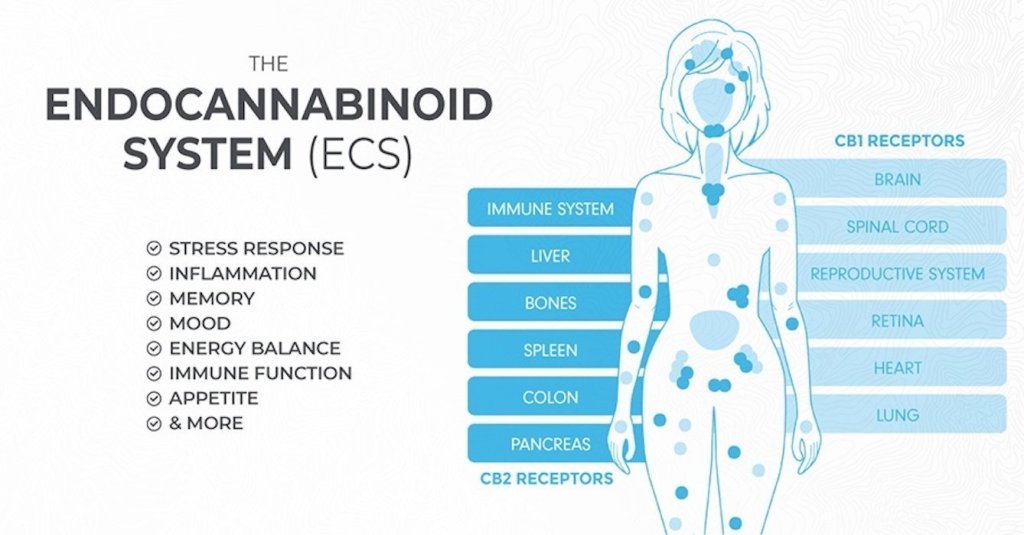
The ECS consists of three parts: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Endocannabinoids are molecules that are naturally made by your body. They’re structurally similar to cannabinoids, which is why cannabinoids are able to bind to the receptors. EC receptors are what the endocannabinoids bind to. Finally, enzymes facilitate the break down of endocannabinoids after they have served their purpose.
What does it do?
The ECS is actually responsible for affecting a multitude of processes:
- Appetite and digestion
- Metabolism
- Pain management
- Inflammation
- Immune system response
- Mood
- Memory and learning
- Motor control
- Sleep
- Cardiovascular function
- Muscle formation
- Bone growth
- Liver function
- Reproductive system function
- Stress
- Skin and nerve function
In other words, the primary role of the ECS is to maintain balance in your body. For example, when you get injured, the ECS kicks in to restore balance to the body.
So, what does this mean?
HHC, THC, and other cannabinoids bind to the body’s endocannabinoid receptors, mimicking the body’s natural endocannabinoids. This is why THC and HHC are linked to pain-relieving, relaxing effects. It also explains how people who use cannabinoid products experience “munchies” or anxiety.
The bottom line
The ECS plays a crucial role in our bodies, but we still have a long way to go before we can fully understand it. As the research for the ECS continues, we might see better cannabinoids being produced or new uses for them being discovered. Whatever the case, our bodies are amazing systems.
Leave a comment